When it comes to Android app development, security and protecting user data are of at most importance. There are several practices that developers should follow.
Maintain Secure communication with other apps
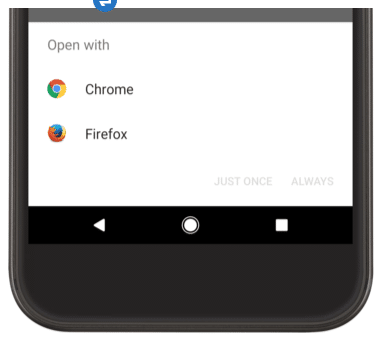
- Use implicit intents to show an app chooser that provides an option to the user to launch at least two possible apps on the device for the requested action. This allows users to transfer sensitive information to the app that they trust.
- Apply signature-based permissions while sharing data between two apps that you control. These permissions do not need user confirmation. Instead, it uses the same signing key for the apps to sign for accessing the data. Hence offer a more streamlined and secure user experience.
<manifest xmlns:android=”http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android”
package=”com.example.myapp”> <
permission android:name=“my_custom_permission_name”
android:protectionLevel=”signature” /> - Non-exported content providers: Unless you intend to send data from your app to other apps. It explicitly disallows other apps to access your ContentProvider in the manifest using android:exported=” false”(by default it is “true” for Android versions lower than 4.4 ).
Secure Network communication
Ensure network security with HTTPS and SSL. For any kind of network communication, we must use HTTPS (instead of plain HTTP) with proper certificate implementation.
- Communication with a web server having a well-known trusted CA certificate does need any additional steps to take while creating the HTTP request.
val url = URL(“https://www.google.com”)
val urlConnection = url.openConnection() as HttpsURLConnection
urlConnection.connect()
urlConnection.inputStream.use {
} - By adding a network security configuration: If your app uses new or custom CAs, you can declare your network’s security settings in a configuration file. This process allows you to create the configuration without modifying any app code. To add a network security configuration file to your app, follow these steps:
- Declare the configuration in your app’s manifest
:<manifest … >
<application
android:networkSecurityConfig=”@xml/network_security_config” … >
<!– Place child elements of <application> element here. —
</application>
</manifest> - Add an XML resource file, located at
res/xm/network_security_config.xml.Specify that all traffic to particular domains should use HTTPS by disabling clear-text:
<network-security-config>
<domain-config cleartextTrafficPermitted=”false”>
<domain includeSubdomains=”true”>secure.example.com</domain> …
</domain-config>
</network-security-config>
During the development process, you can use the<debug-overrides>element to explicitly allow user-installed certificates. This element overrides your app’s security-critical options during debugging and testing without affecting the app’s release configuration. The following snippet shows how to define this element in your app’s network security configuration XML file:
<network-security-config>
<debug-override>
<trust-anchors>
<certificates src=”user” /
</trust-anchors>
</debug-overrides>
</network-security-config>
- Declare the configuration in your app’s manifest
- Create your own trust manager If the web server has a certificate signed by a new or custom CA which is not trusted by the mobile device additionally, you cannot use a network security configuration. For this scenario, you may need to set up a trust manager and handle all SSL warnings that occur.
- Certificates Pinning: Applications can be limited to accepting only a set of certificates by either limiting the set of CAs they trust or by certificate pinning. It is achieved by providing a set of certificates by the hash of the public key (SubjectPublicKeyInfoof the X.509 certificate). A certificate chain is then valid only if the certificate chain contains at least one of the pinned public keys. There are some other factors that should be considered when your application tries to access data through the Internet:
- Use WebView objects carefully: The WebView objects in your app shouldn’t allow users to navigate to sites that are outside of your control. Additionally, JavaScript interface support should be enabled, if you completely control and trust the content in your app’s WebView objects. Use HTML message channels instead of evaluateJavascript() to communicate between a website and your app. Check the Android documentation to see how to secure your WebView.
- Use High-Level Authentication: Authentication mechanisms play a crucial role in mobile application security. Securing sensitive information using multi-factor authentication, robust session management, and a disconnected system. It is also essential to set up advanced authorization with the support of tools such as OAuth 2.0 or JSON web tokens It helps for added security of Android apps.
Provide the right permissions
The app should request only the minimum number of permissions necessary to function properly.
It should not grant permission to complete an action that another app could handle. Instead, use an intent to defer the request to a different app that already has the necessary permission.
For example, if an App requires creating a contact, it delegates the responsibility of contact creation to a contacts app that has already been granted the appropriate WRITE_CONTACTS permission.
Security on data storage
Cryptography is the most efficient way to achieve data security. Hence, Use appropriate Encryption mechanisms while dealing with data inside the app. To achieve greater key security, use the Android Keystore system. The following describes the best practices for storing data on your device.
- Storing private data within internal storage
Users should store all private data within the device’s internal storage, which is sandboxed per app. There is no need to request permission to access these files, and cannot be accessed by other apps. Whenever the user uninstalls an app, the device deletes all files that the app saved within internal storage. Consider working with EncryptedFile objects, which are available from the Security library, instead of File objects. Find the example here: - Use external storage cautiously
The Android system, by default, doesn’t enforce security restrictions on data that resides within external storage, and the device doesn’t guarantee to stay connected to the storage medium itself. Therefore, apply the following security measures to provide safe access to information within external storage.
Use scoped directory access: If your app needs to access only a specific directory within the device’s external storage, use scoped directory access to limit your app’s access to a device’s external storage accordingly.
Access app-specific files: If a file doesn’t contain private or sensitive information but provides value to the user only in your app, store the file in an app-specific directory on external storage. - Store only non-sensitive data in cache files
To provide quicker access to non-sensitive app data, store it in the device’s cache. For caches larger than 1 MB in size, use getExternalCacheDir(); otherwise, use getCacheDir(). Each method provides you with the File object that contains your app’s cached data. - Use SharedPreferences in private mode
To create or access your app’s SharedPreferences objects using getSharedPreferences(), use MODE_PRIVATE so that your app can access the information within the shared preferences file.
Furthermore, developers should use Encrypt SharedPreferences for enhanced security, which wraps the shared preferences class and automatically encrypts keys and values.
Shrink, obfuscate, and optimize your code with the R8 compiler
If you are building your project using Android Gradle plugin 3.4.0 or higher, the plugin no longer uses ProGuard to perform compile-time code optimization. Instead, the plugin works with the R8 compiler to handle the following compile-time tasks:
Code shrinking (or tree-shaking): detects and safely removes unused classes, fields, methods, and attributes from your app and its library dependencies (making it a valuable tool for working around the 64k reference limit).
Resource shrinking: removes unused resources from your packaged app, including unused resources in your app’s library dependencies.
Obfuscation: shortens the name of classes and members, which results in reduced DEX file sizes.
Optimization: inspects and rewrites your code to further reduce the size of your app’s DEX files.
Keep dependencies and libraries up-to-date to make these points of communication more secure.
If you ever want to take your online presence to the next phase, Sreyas IT Solutions can provide you with all the better and latest solutions available. Sreyas is the best software development company. We are the leading Android app development and e-commerce development and design company.